|
Greetings/Γειά σου/泥嚎! My name is Zhihua Liu (Chinese: 刘志华; Greek: Stavros). I am a CHAI Postdoctoral Scholar at the University of Edinburgh, School of Engineering, working with Prof. Sotirios Tsaftaris. I obtained my Ph.D. from University of Leicester. I was really fortunate to spend wonderful time at AstraZeneca Cambridge Center for AI, as research intern working with Dr. Chen Jin and Dr. Amrutha Saseendran. Previously, I served as an algorithm engineer in JD Logistics, JD.com. I received my M.Sc. in Artificial Intelligence from the University of Edinburgh in 2016, my B.Eng. in Internet of Things from University of Science and Technology Beijing in 2015. I spent my undergraduate final year at the School of Computing in University of Dundee, supervised by Prof. Stephen McKenna, Dr. Sebastian Stein and Prof. Jianguo Zhang. CV / Google Scholar / Twitter / Github Email: zliu7 at ed<dot>ac<dot>uk |
 |
|
My research is focusing on medical image analysis, computer vision and machine learning, with recent interests in causal representation learning for visual generation, composition and dynamic perception. |
|
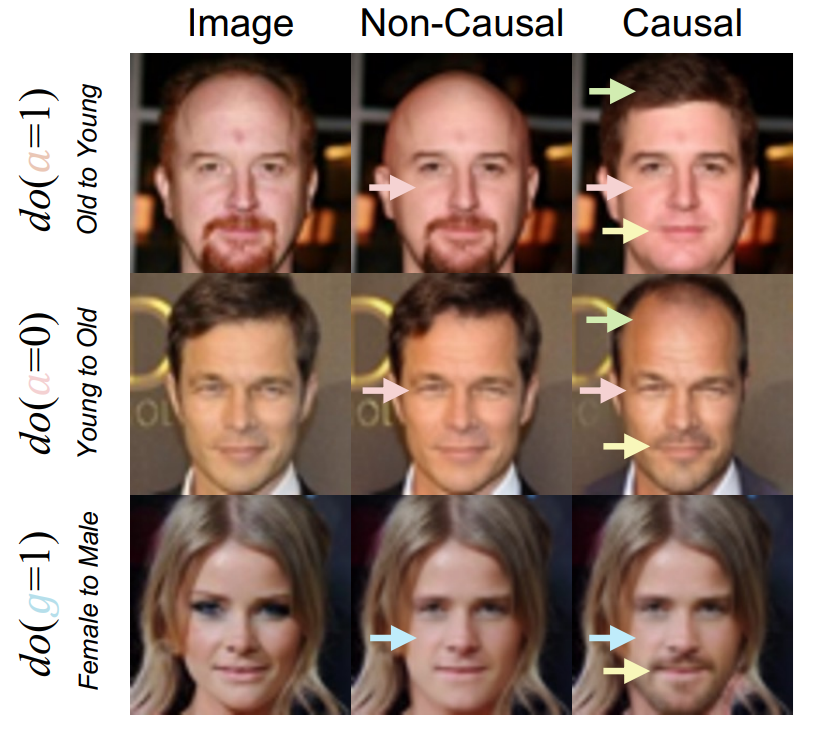
Lei Tong*, Zhihua Liu*, Chaochao Lu, Dino Oglic, Tom Diethe, Philip Teare, Sotirios Tsaftaris, Chen Jin Pre-print, 2025 arXiv We present Causal-Adapter, a modular method that tames frozen text-to-image diffusions for counterfactual image generation. The method enables causal interventions, consistently propagates their effects to dependent attributes and preserves identity. |
|
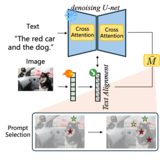
Zhihua Liu, Amrutha Saseendran, Lei Tong, Xilin He, Fariba Yousefi, Nikolay Burlutskiy, Dino Oglic, Tom Diethe, Philip Teare, Huiyu Zhou, Chen Jin ICML International Conference on Machine Learning, 2025 arXiv / Project Page / Poster We introduce Segment Anyword, a training-free visual prompt learning framework with test-time inversed adaption for open-set language grounded segmentation, where visual prompts are simultaneously regularized by linguistic structual information. |
|
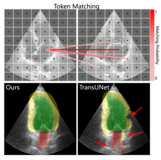
Zhihua Liu, Lei Tong, Xilin He, Che Liu, Rossella Arcucci, Chen Jin, Huiyu Zhou BMVC British Machine Vision Conference, 2025 arXiv / Code / Poster We proposes BOTM, a novel echocardiography segmentation network leveraging visual token anatomical consistency from a transportation perspective. |
|
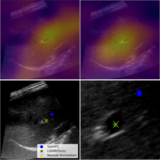
Zhihua Liu, Bin Yang, Yan Shen, Xuejun Ni, Sotirios Tsaftaris, Huiyu Zhou MedIA Medical Image Analysis, 2024 arXiv / Code / Poster Accurate tracking of an anatomical landmark over time has been of high interests for disease assessment such as minimally invasive surgery and tumor radiation therapy. In this paper, we propose a long-short diffeomorphic motion network, which is a multi-task framework with a learnable deformation prior to search for the plausible deformation of landmark. |

|
Zhihua Liu, Lei Tong, Zheheng Jiang, Long Chen, Feixiang Zhou, Qianni Zhang, Xiangrong Zhang, Yaochu Jin, Huiyu Zhou CAIS Complex & Intelligent Systems, 2022 arXiv / code Considering stateof-the-art technologies and their performance, the purpose of this paper is to provide a comprehensive survey of recently developed deep learning based brain tumor segmentation techniques. |
|
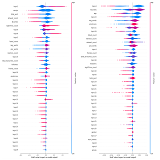
Lei Tong, Zhihua Liu, Zheheng Jiang, Feixiang Zhou, Long Chen, Jialin Lyu, Xiangrong Zhang, Qianni Zhang, Abdul Sadka, Yinhai Wang, Ling Li, Huiyu Zhou IEEE TAE IEEE Trans. on Affective Computing, 2022 arXiv / code / Media A novel classifier, namely, Cost-sensitive Boosting Pruning Trees (CBPT), which demonstrates a strong classification ability on two publicly accessible Twitter depression detection datasets.. |
|
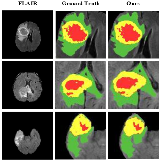
Zhihua Liu, Lei Tong, Long Chen, Feixiang Zhou, Zheheng Jiang, Qianni Zhang, Yinhai Wang, Caifeng Shan, Ling Li, Huiyu Zhou IEEE TMI IEEE Trans. on Medical Imaging, 2021 arXiv / code A novel approach named Context-Aware Network (CANet) for brain glioma segmentation. |
|
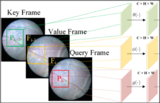
Zhihua Liu MPhil Thesis, 2020 arXiv / Poster Benefited from deep learning techniques, remarkable progress has been made within the medical image analysis area in recent years. However, it is very challenging to fully utilize the relational information (the relationship between tissues or organs or images) within the deep neural network architecture. Thus in this thesis, we propose two novel solutions to this problem called implicit and explicit deep relational learning. We generalize these two paradigms of deep relational learning into different solutions and evaluate them on various medical image analysis tasks. |
|
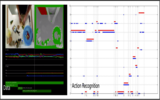
Zhihua Liu BEng Thesis, 2015 PDF / Poster / Dataset The recognition of human action is widely applied in video surveillance, virtual reality and in some human-computer interaction areas such as user experience designing tasks. Pattern recognition becomes a hot topic in the field of computer vision. In this report, I summarize human behavior recognition problem as a problem of acquiring computing data through motion detection and symbolic acting information. Then extract and understand the behavior of the action features to achieve classification target. On this basis, I review the moving object detection, motion feature extraction and movement characteristics to understand the technical analysis, the correlation method classification, and discuss the difficulties and research directions of this project. |
|
|
|
2020-2023
CO1104 Computer Architecture CO4105 Advanced C++ Programming CO3002 Analysis and Design of Algorithms 2019-2020 FS0023 STEM Foundation Year Lab-Physics |
|
|
|
I like traveling and photography. Here is my instagram.
I also like sports, especially football ⚽ and table tennis 🏓. I started to receive professional table tennis training from the age of 5, got into the school team, and gave up training in high school because of the college entrance examination. |
|
This website template is from Jon Barron. |